Galway
|
This article needs additional citations for verification. (May 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message)
|
| Galway Gaillimh
|
||
|---|---|---|
| City | ||

Eyre Square
|
||
|
||
| Nickname(s): "City of the Tribes" | ||
| Motto: Laudatio Ejus Manet In Secula Seculorum[1] (Latin) "His Praise Remains unto Ages of Ages" |
||
| Galway City in Ireland | ||
| Coordinates: 53°16′19″N 9°2′56″W / 53.27194°N 9.04889°WCoordinates: 53°16′19″N 9°2′56″W / 53.27194°N 9.04889°W | ||
| Country | Ireland | |
| Province | Connacht | |
| County | ||
| Charter awarded | 1484 | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Galway City Council | |
| • Mayor of Galway | Noel Larkin[2] | |
| • LEAs | 3 | |
| • Dáil Éireann | Galway West | |
| • European Parliament | Midlands–North-West | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 53 km2 (20 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 25 m (82 ft) | |
| Population (2016) | ||
| • Total | 79,934 (including suburbs) | |
| • Rank | 4th | |
| • Density | 1,508.1/km2 (3,906/sq mi) | |
| Demonym(s) | Galwegian, Tribesman | |
| Time zone | WET (UTC0) | |
| • Summer (DST) | IST (UTC+1) | |
| Eircode (Routing Key) | H91 | |
| Area code(s) | +353 (0)91 | |
| Vehicle registration | G | |
| Irish Grid Reference | M344255 | |
| Website | www |
|
Galway (/ˈɡɔːlweɪ/; Irish: Gaillimh, pronounced [ˈɡalʲɪvʲ]) is a city in the West of Ireland in the province of Connacht. Galway City Council is the local authority for the city. Galway lies on the River Corrib between Lough Corrib and Galway Bay and is surrounded by County Galway. It is the fourth most populous urban area in the Republic of Ireland and the sixth most populous city in the island of Ireland.
According to the 2016 Irish Census, Galway city has a population of 79,504; however, the rural county agglomeration is far more populous.[3]
Galway will be European Capital of Culture in 2020, alongside Rijeka, Croatia.
Name[edit]
The city's name is from the Irish name for Gaillimhe ("Galway"), which formed the western boundary of the earliest settlement, Dún na Gaillimhe "Fort Gaillimh".[4] (Mythical and alternative derivations of the name are given in History of Galway).
Historically, the name was Anglicised as Galliv,[5] which is closer to the Irish pronunciation as is the city's name in Latin, Galvia.
The city also bears the nickname "The City of the Tribes" (Irish: Cathair na dTreabh) because of the fourteen merchant families called the "tribes of Galway"[6] led the city in its Hiberno-Norman period.
Residents of the city refer to themselves as "Galwegians".
History[edit]

Dún Bhun na Gaillimhe ("Fort at the Mouth (bottom) of the Gaillimh") was constructed in 1124, by the King of Connacht, Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair (1088–1156). Eventually, a small settlement grew up around this fort. During the Norman invasion of Connacht in the 1230s, Galway fort was captured by Richard Mor de Burgh, who had led the invasion. As the de Burghs eventually became Gaelicised, the merchants of the town, the Tribes of Galway, pushed for greater control over the walled city.[citation needed]
| Historical population | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1813 | 24,684 | — |
| 1821 | 27,775 | +12.5% |
| 1831 | 33,120 | +19.2% |
| 1841 | 17,275 | −47.8% |
| 1851 | 20,055 | +16.1% |
| 1861 | 16,048 | −20.0% |
| 1871 | 15,597 | −2.8% |
| 1881 | 15,471 | −0.8% |
| 1891 | 13,800 | −10.8% |
| 1901 | 13,426 | −2.7% |
| 1911 | 13,255 | −1.3% |
| 1926 | 14,227 | +7.3% |
| 1936 | 18,294 | +28.6% |
| 1946 | 20,370 | +11.3% |
| 1951 | 21,316 | +4.6% |
| 1956 | 21,366 | +0.2% |
| 1961 | 23,700 | +10.9% |
| 1966 | 26,295 | +10.9% |
| 1971 | 29,375 | +11.7% |
| 1981 | 41,861 | +42.5% |
| 1986 | 47,104 | +12.5% |
| 1991 | 50,853 | +8.0% |
| 1996 | 57,363 | +12.8% |
| 2002 | 66,163 | +15.3% |
| 2006 | 72,729 | +9.9% |
| 2011 | 75,529 | +3.8% |
| 2016 | 79,504 | +5.3% |
| [7] | ||
This led to their gaining complete control over the city and to the granting of mayoral status by the English crown in December 1484. Galway endured difficult relations with its Irish neighbours. A notice over the west gate of the city, completed in 1562 by Mayor Thomas Óge Martyn, stated "From the Ferocious O'Flahertys may God protect us". A by-law forbade the native Irish (as opposed to Galway's Hiberno-Norman citizens) unrestricted access into Galway, saying "neither O’ nor Mac shall strutte nor swagger through the streets of Galway" without permission.
During the Middle Ages, Galway was ruled by an oligarchy of fourteen[6] merchant families (twelve who claimed to be of Norman origin and two of Irish origin). These were the "Tribes of Galway". The city thrived on international trade, and in the Middle Ages, it was the principal Irish port for trade with Spain and France. The most famous reminder of those days is ceann an bhalla ("the end of the wall"), now known as the Spanish Arch, constructed during the mayoralty of Wylliam Martin (1519–20). In 1477 Christopher Columbus visited Galway, possibly stopping off on a voyage to Iceland or the Faroe Islands. Seven or eight years later, he noted in the margin of his copy of Imago Mundi:
Men of Cathay have come from the west. [Of this] we have seen many signs. And especially in Galway in Ireland, a man and a woman, of extraordinary appearance, have come to land on two tree trunks [or timbers? or a boat made of such?]
The most likely explanation for these bodies is that they were Inuit swept eastward by the North Atlantic Current.[4]
During the 16th and 17th centuries Galway remained loyal to the English crown for the most part, even during the Gaelic resurgence, perhaps for reasons of survival. However, by 1642 the city had allied itself with the Catholic Confederation of Kilkenny during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. During the resulting Cromwellian conquest of Ireland, Cromwellian forces captured the city after a nine-month siege. At the end of the 17th century the city supported the Jacobites in the Williamite war in Ireland and was captured by the Williamites after a very short siege not long after the Battle of Aughrim in 1691. The great families of Galway were ruined. The city suffered further under the potato famines of 1845–1852, and it did not fully recover until the period of strong economic growth of the late 20th century (see Celtic Tiger).
Religion[edit]
In common with many ancient European sea ports, the patron saint of the city (since the 14th century) is St Nicholas of Myra. The Roman Catholic diocese of Galway was created in 1831 AD following the abolition by the Holy See of the Wardenship of Galway. It was united with the diocese of Kilmacduagh (est. 1152 AD) and given the administratorship of the diocese of Kilfenora (est. 1152 AD) in 1883. Its full name is the Diocese of Galway, Kilmacduagh and Apostolic Administratorship of Kilfenora (in Irish - Deoise na Gaillimhe, Chill Mac Duach agus Riarachán Aspalda Cill Fhionnúrach, in Latin - Diocesis Galviensis, Duacensis ac Administratio Apostolica Finaborensis). The diocese is under the patronage Our Lady Assumed into Heaven and St Nicholas (Galway), Saint Fachanan (Kilmacduagh) and St Colman (Kilfenora). As the diocese of Kilfenora is in the Ecclesiastical Metropolitan Province of Cashel the Bishop of Galway is its Apostolic Administrator rather than its bishop. The dioceses of Galway and Kilmacduagh are in the Ecclesiastical Metropolitan Province of Tuam. The current bishop is Most Rev. Martin Drennan, installed 3 July 2005. Of the 38 parishes in the RC diocese 14 are situated in the City and are divide into two deaneries - the deanery of Galway City West and of Galway City East. In each deanery a Vicar Forane exercises limited jurisdiction on behalf of the bishop.
In the Church of Ireland, Galway is a parish of the United Diocese of Tuam, Killala and Achonry. The principal church of the parish is the St. Nicholas' Collegiate Church (founded 1320). Russian, Romanian, Coptic, and Mar Thoma Syrian Orthodox Churches use the facilities of St Nicholas Collegiate Church for their services. The Ahmadiyya-run Galway Mosque, opened in 2014, is the only purpose-built mosque in Galway.[8]
Politics[edit]
Local government[edit]
With a population of 75,529, Galway is the fourth most populous city in the State and the 23rd most populous area of local government.[9] Services such as waste collection, recycling, traffic control, parks and housing are controlled by a fifteen-member city council elected to five-year terms by proportional representation through means of the Single Transferable Vote PR-STV. The City Council is chaired by a mayor who is elected to a one-year term by fellow councillors. The role of mayor is mainly ceremonial, although they do have the casting vote. The first mayor was Peirce Lynch Fitzjohn, elected in 1485. Cllr. Frank Fahy was elected Mayor in June 2015.
The symbols of the office of the Mayor and the emblems of the dignity of the City Council are the Civic Sword (1620s) and the Great Mace (1710) which are carried in procession before the Mayor and Council on solemn civic occasions. When not in ceremonial use they can be seen at the Galway City Museum. In 1579, Queen Elizabeth I confirmed the city's charter and appointed the Mayor as 'Admiral of the Bay and of the Aran islands'. The title, though extant, is rarely used except for purely ceremonial purposes.[citation needed]
Galway City is part of the Galway West constituency of Dáil Éireann. Its TDs are:
- Noel Grealish (Independent). A Native of An Carn Mór.
- Catherine Connolly (Independent). Former Mayor of Galway, and Galway based.
- Éamon Ó Cuív (Fianna Fáil). Corr na Móna (Conamara) based. He is a former Minister for Social Protection.
- Hildegarde Naughton (Fine Gael). Former Senator and City Councillor.
- Seán Kyne (Fine Gael). Based in Moycullen. Former County Councillor.
President of Ireland Michael D. Higgins was TD for the Galway West parliamentary constituency, of which Galway City is a part, from 1981 to 1982 and from 1987 to 2011. He was also Mayor of Galway for two terms, 1981–82 and 1990-91.[citation needed]
The highest honour the city can bestow is the Freedom of the City. Among the names on the Roll of Honour are: Douglas Hyde, President of Ireland, 1939; Eamonn de Valera, Taoiseach, 1946; Sean T O'Kelly, President of Ireland, 1950; Robert F. Wagner, Mayor of New York, 1961; John F. Kennedy, President of the US, 1963; Pope John Paul II, 1979; Ronald Reagan, President of the US, 1984; Hillary Clinton, 1999; Richard M. Daley, Mayor of Chicago, 2003; Nelson Mandela, 2003; Aung San Suu Kyi, Burmese activist/leader, 2005; Garry Hynes, Druid Theatre Founder, 2006; and Michael D. Higgins, President of Ireland, 2012.[citation needed]
The courts[edit]
Galway's District Court is the main court of summary jurisdiction and hears minor cases without a jury. It is responsible for hearing small civil claims, certain family law cases, administers the liquor licensing laws and is responsible for indicting the accused and sending them forward for trial at the Circuit Court and the Central Criminal Court. The Circuit Court in Galway tries all indictable offences (those cases triable by a judge and jury), except murder, rape, treason, piracy and genocide, which are reserved to the Central Criminal Court. It can also hear appeals from the District Court. Its decisions can be appealed to the Court of Criminal Appeal. Civilly, the court is limited to compensation claims of not more than €75,000. Both parties may waive this amount and grant the court unlimited jurisdiction. Divorce, Judicial Separation and probate cases can be heard provided they are within the financial parameters of the courts jurisdiction. Decisions in civil cases can be appealed to the High Court.[citation needed]
The High Court sits four times a year in Galway to hear original actions (actions that are not appeals from lower courts). It also sits twice a year in Galway to hear appeals from the Circuit Court in civil and family law cases. Its decisions can be appealed to the Supreme Court which sits only in Dublin.[citation needed]
Climate[edit]
Galway has a year-round mild, moist, temperate and changeable climate, due to the prevailing winds of the North Atlantic Current. The city does not experience temperature extremes, with temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F) and above 30 °C (86 °F) being rare. The city receives an average of 1,156 mm (45.51 in) of precipitation annually, which is evenly distributed throughout the year. The average January temperature in the city is 5.9 °C (43 °F) and the average July temperature is 15.9 °C (61 °F). This means that Galway, like most of Ireland, has a Maritime Temperate climate (Cfb) according to the Köppen climate classification system. While extreme weather is rare, the city and county can experience severe windstorms that are the result of vigorous Atlantic depressions that occasionally pass along the north west coast of Ireland. Most of these storms occur between late autumn and early spring. Due to the city's northerly location and its longitude, Galway has long summer days. Daylight at midsummer is before 04:20 and lasts until after 23:00. In midwinter, daylight does not start until 08.49, and is gone by 16:19.
| Climate data for Galway (1981–2010 averages) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 8.7 (47.7) |
9.1 (48.4) |
10.8 (51.4) |
13.0 (55.4) |
15.8 (60.4) |
17.8 (64) |
20.5 (68.9) |
19.1 (66.4) |
17.3 (63.1) |
14.1 (57.4) |
11.0 (51.8) |
9.0 (48.2) |
13.8 (56.8) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.0 (42.8) |
6.2 (43.2) |
7.8 (46) |
9.3 (48.7) |
11.9 (53.4) |
14.2 (57.6) |
16.1 (61) |
15.8 (60.4) |
13.9 (57) |
11.0 (51.8) |
8.1 (46.6) |
6.3 (43.3) |
10.6 (51.1) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 3.5 (38.3) |
3.8 (38.8) |
4.9 (40.8) |
5.8 (42.4) |
8.0 (46.4) |
10.6 (51.1) |
12.9 (55.2) |
12.5 (54.5) |
10.4 (50.7) |
7.9 (46.2) |
5.1 (41.2) |
3.6 (38.5) |
7.3 (45.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 114 (4.49) |
94 (3.7) |
92 (3.62) |
61 (2.4) |
68 (2.68) |
81 (3.19) |
69 (2.72) |
109 (4.29) |
93 (3.66) |
130 (5.12) |
124 (4.88) |
121 (4.76) |
1,156 (45.51) |
| Source #1: WMO | |||||||||||||
| Source #2: ECA&D | |||||||||||||
Places of interest[edit]
|
This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2016) (Learn how and when to remove this template message)
|


- Lynch's Castle on Shop Street is a medieval town house, now a branch of Allied Irish Banks.
- The Church of Ireland St. Nicholas' Collegiate Church is the largest medieval church still in everyday use in Ireland.[citation needed] It was founded in 1320 and enlarged in the following two centuries.
- The Cathedral of Our Lady Assumed into Heaven and St Nicholas was consecrated in 1965 and is a far larger building constructed from limestone. It has an eclectic style, with a Renaissance Revival dome, pillars and round arches, and a Romanesque Revival portico that dominates the main façade – which is an unusual feature in modern Irish church building.
- The original quadrangle building of National University of Ireland, Galway which was erected in 1849 (during the Great Famine or An Gorta Mór) as one of the three colleges of the Queen's University of Ireland (along with Queen's University Belfast and University College Cork). The university holds the UNESCO archive[citation needed] of spoken material for the Celtic languages.
- Hotel Meyrick, originally the Railway Hotel and then the Great Southern Hotel, built by the Great Southern Railway Company in 1845.[10] Sitting at the southern perimeter of Eyre Square, it is the City's oldest hotel still in operation.
- The remains of Menlo Castle can be seen outside the city, on the eastern bank of the River Corrib. It was one of the ancestral homes of the Blake family, one of the Tribes of Galway from c. 1600-1910. The façade of the family's townhouse ("Blake's Castle") is still extant next to Jury's Hotel at the bottom of Quay Street.
- Eglinton Canal, named after a former Lord Lieutenant of Ireland, joins the River Corrib to the sea, and flows for just more than a kilometre from the University to the Claddagh.
- The Claddagh is the oldest part of Galway but little or nothing remains of its old thatched village. However, in a side altar of the parish church, St Mary's on the Hill, is the late medieval statue of Our Lady of Galway. The ancient ritual of the Blessing of the Bay takes place on the Sunday nearest the feast of the Assumption.
- The Browne doorway, originally located on Lower Abbeygate Street but now standing at the north end of Eyre Square, was the doorway to the townhouse of the Browne family, one of the fourteen Tribes of Galway.
- The Lynch Window, (on Market Street), at which is a plaque commemorating one of the city's legends. According to legend, in 1493, the then Mayor, James Lynch FitzStephen, hanged his own son for the murder of a young Spanish visitor who had the misfortune to befriend the girlfriend of the Mayor's son.[11]
- The Hall of the Red Earl (Halla an Iarla Rua) can be viewed through a protective glass wall off Flood Street. It is the earliest medieval settlement fragment surviving within the walls of the city. It was built by the de Burgo family in the 13th century and was a key municipal building for the collection of taxes, dispensation of justice and hosting banquets. It was the medieval equivalent of tax office, court house and town hall.
Museums[edit]
The Galway City Museum features two parts, "Fragments of a City" and "On Reflection." "Fragments of a City"'s collection is mainly about the heritage of Galway, while "On Reflection" is a collection of the most important Irish artists from the second half of the 20th century. This museum was designed to allow tourists and local visitors to really get to understand and know the city of Galway. This museum also houses the statue of the poet, Pádraic Ó Conaire which was originally located in the Kennedy Park section of Eyre Square, prior to the Square's renovation. Visitors can also view the silver Civic Sword and Great Mace of the city at the museum. The museum is part of the Spanish Arch, the historical remnants of the 16th century wall that helped protect Galway.[12]
The James Mitchell Museum of Geology in NUIG is a restored 19th century museum "within a museum".
The Computer & Communications Museum of Ireland is also housed in NUIG.
The Nora Barnacle House Museum in Bowling Green is the smallest museum in Ireland. Nora was the lover, companion and, later, wife of writer James Joyce.
Cemeteries[edit]
Fort Hill Cemetery, on Lough Athalia Road, is the oldest cemetery still in use in Galway City. Inside the main gate is a memorial to sailors of the Spanish Armada who were buried here in the 1580s.
Rahoon Cemetery (officially known as Mount St. James Cemetery), Rahoon Road, on the western edge of the city affords splendid panoramic views of the city.
Among the notable persons buried here are:
- Michael Bodkin, an admirer of Nora Barnacle, the wife of James Joyce, who was the inspiration for the character, "Michael Furey" in the story The Dead from Dubliners
- Michael Feeney, the "lover" in Joyce's poem She Weeps Over Rahoon
- the actress Siobhan McKenna.
Bohermore Cemetery (or the New Cemetery, as it is more popularly known), Cemetery Cross, Bohermore, was opened in 1880. It contains two mortuary chapels and is the burial place of several important Galwegians, including Pádraic Ó Conaire the gaelic author, William Joyce, more widely known as Lord Haw-Haw the Nazi propagandist, Augusta, Lady Gregory, co-founder of the Abbey Theatre in Dublin and Michael Morris, 3rd Baron Killanin, a senior member of one the Tribes of Galway and former world president of the International Olympic Committee. A memorial to the 91 people who died on 14 August 1959 when Dutch aeroplane KLM Flight 607-E crashed into the sea 180 km (112 mi) west of Galway can be seen just inside the main gates. Several bodies of the passengers are buried around the memorial.
There are several smaller cemeteries within the city boundaries. Some are no longer in use or are used primarily by families with ancient burial rights. These are St James's Cemetery (Teampall) in Glenina Heights, Menlo Cemetery near Menlo Castle, Ballybrit Graveyard near the entrance to Galway Racecourse, and a very ancient early Christian graveyard at Roscam near Merlin Park. Several city churches have graveyards attached which were formerly used for the interment of clergy and parishioners - Castlegar Church, Claddagh Church', St Patrick's Church on Forster Street and St. Nicholas' Collegiate Church. Several bishops are buried in the crypt below the RC Cathedral but this not usually open to the public.
Culture[edit]

Galway is known as Ireland's Cultural Heart (Croí Cultúrtha na hÉireann)[13] and is renowned for its vibrant lifestyle and numerous festivals, celebrations and events.[14] Every November, Galway hosts the Tulca Festival of Visual Arts [15] as well as numerous festivals.
On 1 December 2014, the Director General of UNESCO announced the official designation of Galway as a UNESCO City of Film.
In 2004, there were three dance organisations, ten festival companies, two film organisations, two Irish language organisations, 23 musical organisations, twelve theatre companies, two visual arts groups, and four writers' groups based in the city.[16]
Furthermore, there were 51 venues for events, most of which were specialised for a certain field (e.g. concert venues or visual arts galleries), though ten were described as being 'multiple event' venues.[16] The main squares in the city are Eyre Square (containing John F. Kennedy Park) in the centre of the city, and Spanish Parade next to the Spanish Arch.
In 2007, Galway was named as one of the eight "sexiest cities" in the world.[17] A 2008 poll ranked Galway as the 42nd best tourist destination in the world, or 14th in Europe and 2nd in Ireland (behind Dingle). It was ranked ahead of all European capitals except Edinburgh, and many traditional tourist destinations (such as Venice).[18] The New Zealand Herald listed Galway as one of 'five great cities to visit in 2014'.
Irish language[edit]
Galway City has a reputation among Irish cities for being associated with the Irish language, music, song and dancing traditions. It is sometimes referred to as the 'Bilingual Capital of Ireland', although like elsewhere in the Republic of Ireland, inhabitants converse mostly in English. The city is well known for its "Irishness", mainly because it has on its doorstep the Galway Gaeltacht. Irish theatre, television and radio production and Irish music form a component of Galway city life, with both An Taibhdhearc, the National Irish Language Theatre, in Galway city itself, while TG4 and RTÉ Raidió na Gaeltachta headquarters are in the Connemara Gaeltacht elsewhere in County Galway. Four electoral divisions, or neighbourhoods (out of twenty-two), are designated as Gaeltachtaí.[16] NUI Galway also holds the archive of spoken material for the Celtic languages.[19]
The Claddagh[edit]
On the west bank of the River Corrib as it enters the sea is the ancient neighbourhood of The Claddagh. For centuries it was an Irish-speaking enclave outside the city walls. Claddagh residents were mainly fisher folk and were governed by an elected 'King'. The King of the Claddagh settled or arbitrated disputes among the locals and had the privilege of a white sail on his fishing boat. The last true king, Martin Oliver, died in 1972. The title is still used but in a purely honorary and ceremonial context. The current King is Michael Lynskey. The area is also famous for its association with the Claddagh Ring.
The arts[edit]
Literature[edit]
Among the poets currently writing in Galway are Fred Johnston, Patrick Deeley, Rita Ann Higgins, Mary O'Malley, Moya Cannon, Eva Bourke, Kevin Higgins, Ndrek Gjini, Elaine Feeney. Walter Macken, Eilís Dillon, Máirtín Ó Direáin, Máirtín Ó Cadhain, Liam O'Flaherty, Pádraic Ó Conaire and Ken Bruen are well-known writers in both English and Irish with a connection to Galway. The writer and publisher Frank Harris was born in Galway.
The James Hardiman Library at NUI Galway houses around 350 archived and/or digitised collections including the Thomas Kilroy Collection, the Brendan Duddy Papers on the Northern Ireland conflict, the John McGahern archive and the manuscript Minutes of Galway City Council from the 15th to mid-19th centuries.
Among the literary magazines published in Galway are The Galway Review, which is Galway's leading literary magazine, Crannóg Magazine, which describes itself as 'Ireland's premier independent fiction and poetry magazine since 2002' and ROPES, an annual literary journal published by students of the MA in Literature and Publishing at NUI Galway.
Gretta Conroy, in James Joyce's short story The Dead, remembers her lover Michael Furey throwing stones against the window of her grandmother's house on Nun's Island, in the city. The poem, She Weeps Over Rahoon by James Joyce, tells of the grief of Joyce's wife, Nora Barnacle, over the death of her onetime boyfriend Michael Bodkin. Both Bodkin and Nora were from Galway and Bodkin is buried in Rahoon Cemetery in the western suburbs of the city.[20]
Walter Macken's novel Rain on the Wind is set in the city as are the "Jack Taylor" crime novels of Ken Bruen.
Early 16th-century Galway features in several of the "Burren mysteries" of Cora Harrison.[21]
Theatre[edit]
Galway has a permanent Irish language theatre located in the city centre, Taibhdhearc na Gaillimhe (1928), which has produced some of Ireland's most celebrated actors. The Druid Theatre Company has won international acclaim for its cutting edge production and direction.
There are many theatres in the city including Nun's Island Theatre, The Bank of Ireland Theatre, The Druid Lane Theatre, The Black Box Theatre and The Town Hall Theatre, a modern art theatre with two performance spaces opened in 1995[22] that has a 52-week program covering all aspects of the performing arts including ballets, musicals and operas. It has been the venue for many Irish film premieres, during the Galway Film Fleadh.
Two of the most celebrated Irish actors of the 20th century, Siobhán McKenna and Peter O'Toole, have strong family connections with Galway. Other well-known actors include Mick Lally, Seán McGinley and Marie Mullen, all three of whom were founders of the Druid Theatre Company. Other actors with strong Galway connections are Pauline McLynn, (Shameless and Father Ted), Nora Jane Noone and Aoife Mulholland.
Garry Hynes, first artistic director of Druid Theatre, was the first woman ever to win a Tony Award for direction.
Music[edit]

Galway has a vibrant and varied musical scene. As in most Irish cities traditional music is popular and is kept alive in pubs and by street performers. Galway Early Music Festival presents European music from the 12th to the 18th century. It encourages not only music, but also dance and costumes. The festival involves both professional and amateur musicians.[23]
Galway Cathedral Recitals is an international series of concerts of classical music which has taken place in Galway Cathedral each July and August since 1994.[24]
A number of notable choirs are based in the city. They include Tribal Chamber Choir (founded in 2009) directed by Mark Keane;[25] the Galway Baroque Singers (founded in 1983) directed by Audrey Corbett; Cois Cladaigh Chamber Choir (founded in 1982) directed by Brendan O'Connor, which sang at the inauguration of President Michael D. Higgins in St Patrick's Hall, Dublin Castle, on 11 November 2011; Galway Gospel Choir (founded in 2001) directed By Michel Durham Brandt; and Galway Choral Association (founded in 1998) directed by Norman Duffy. In addition to its parish choir the Collegiate Church of St Nicholas is home to two other choral groups, the Choral Scholars (adult) and the Schola Cantorum (juvenile).
The Galway Arts Festival (Féile Ealaíon na Gaillimhe) takes place in July. It was first held in 1978 and since then has grown into one of the biggest arts festivals in Ireland. It attracts international artists as well as providing a platform for local and national performers. The festival features parades, street performances and plays, musical concerts and comedy acts. Highlights of the festival tend to be performances by Macnas and Druid Theatre Company, two local performance groups. The Galway Youth Orchestra was formed in 1982.
The renowned folk and traditional singer Dolores Keane lives in Galway.
Traditional Irish music[edit]
Galway city is a major centre for traditional Irish music. The traditional group De Dannan were based in Galway. Musicians such as Mickey Finn, Frankie Gavin, Johnny (Ringo) McDonagh, Alec Finn, Máirtín O'Connor and Gerry Hanley were born or came to prominence in Galway. Carl Hession, a well known Irish composer, arranger and traditional musician also hails from Galway city.
Comhaltas branches operate in several parts of the city, teaching Irish Traditional Music to children. Dusty Banjos runs classes and sessions in the city for adults switching from other musical traditions to Irish Traditional Music, and for adult beginners and improvers who are not at a level where they could participate in general sessions.
Live Music venues[edit]
Traditional and contemporary music can be heard at numerous locations around the city. Among the more notable are The Crane Bar on Sea Road, Tigh Neachtáin Quay Street and Róisín Dubh on Lr Dominic Street.
Pop music[edit]
The girls from Galway have inspired many artist, most notable are Steve Earle (Galway Girl (2000)) and Ed Sheeran (Galway Girl (2017))
Entertainment[edit]
Cinema[edit]
Galway has three cinema complexes within easy reach of the city centre. The 11 screen IMC cinema is across the road from the Galway Shopping Centre, Headford Road. The 9 screen EYE cinema, is at Wellpark, Dublin Road. There is a six-screen IMC complex in Oranmore.
On 1 December 2014, Galway was granted designation as a Unesco "City of Film".[26]
Galway is home to the Galway Film Fleadh, Ireland's foremost film festival, which takes place over six days each July. The Galway Film Fleadh is a platform for international cinema in Ireland and an advocate for Irish national cinema, for which the festival's identity has become synonymous.[27] The Galway Film Fleadh is an industry festival, with many industry events taking place under the name of the Galway Film Fair, including conferences, screenings, masterclasses, networking events, Ireland’s longest-running Pitching Competition and Ireland’s only film marketplace.[28]
In 2014, a MovieMaker magazine panel of U.S. filmmakers, critics and industry executives included the Galway Film Fleadh on its list of the "25 Coolest Film Festivals in the World".[29]
Events and festivals[edit]

Many sporting, music, arts and other events take place in the city. The largest of these annual events begins with the Galway Film Fleadh and the Galway Arts Festival in July, the Galway Races in August, and the Galway International Oyster Festival in September. Other events include the Fleadh Imboilg, the Baboró International Children's Festival, the Cúirt International Festival of Literature, the Galway Early Music Festival,[30] Seachtain na Gaeilge (March), Salthill Air Show (June), the Colours Fringe Festival, Little Havana Festival, the Galway Sessions,[31] Galway Garden Festival,[32] Galway Comedy Festival, Baffle Poetry Festival, Galway Aboo Halloween Festival, Tulca Festival of Visual Arts, Galway Science and Technology Festival, Spirit of Voice Festival, Galway Christmas Market,[33] Galway African Film Festival and Galway Pride Festival.[34]
In June 2010, the Super8 Shots film festival was launched in Galway, the first Super 8 mm (0.31 in) film festival to occur in Ireland.[35]
Each year in November, Galway hosts The Irish Fly Fair and Angling Show, this Fly Fishing Event brings together Fly Dressers, Fly Casters and Fishing Celebrities from many different countries, to show of their craft.[36]
Media[edit]
Radio[edit]
There are only two radio stations based in the city – Galway Bay FM (95.8 FM) broadcasts from the city to the whole county; Flirt FM (101.3 FM) the student radio station for NUIG.
Print[edit]
One of the main regional newspapers for the county is The Connacht Tribune which prints two titles every week, the Connacht Tribune on Thursday, and the Galway City Tribune on Friday. As of January 2007, The Tribune has a weekly readership of over 150,000. Another Galway-based newspaper is the Galway Advertiser, a free paper printed every Thursday with an average of 160 pages and a circulation of 70,000 copies. It is the main paper of the Advertiser Newspaper Group which distributes 200,000 newspapers per and more week to a variety of other Irish cities and towns. Another free paper, the Galway Independent, prints on a Tuesday night for Wednesday circulation.
Online[edit]
Being a city of culture, Galway has a dedicated hub for all cultural events and organisations. Galway Hub is a free resource for both practitioners and the general public in which to engage with the arts and cultural events across the city and county.[37]
Demographics[edit]
| Electoral Division | Population |
|---|---|
| Galway City | |
| Galway City West | 26,189 |
| Galway City Central | 23,169 |
| Galway City East | 25,698 |
| TOTAL | 75,529 |
| County Galway | |
| Na Forbacha | 1,311 |
| Bearna | 3,630 |
| Maigh Cuillin | 2,008 |
| Galway Rural | 126 |
| Ceathrú an Bhrúnaigh | 918 |
| Baile Uí Chláir | 2,042 |
| An Carn Mór | 2,609 |
| Baile an Teampaill | 1,462 |
| Oranmore | 4,325 |
| Clarinbridge | 3,271 |
| Eanach Dhúin | 1,860 |
| TOTAL | 23,562 |
Preliminary information from the 2011 census shows Galway City has a population of 75,414, and increase of 3,000 over the 2006 census figures.[38]
Based in the 2006 census, the population of Galway City and its environs was 72,729, of which 72,414 lived in the city limits and 315 live in the city's environs in County Galway.[39] If the current growth rate continues, the population of the city will hit 100,000 by 2020.[40] Galway City is the fourth largest in the Republic of Ireland, and sixth on the island of Ireland.
Approximately 80% of the population of Galway is white Irish, descended from native Gaelic peoples and Norman settlers. A further 2.9% are Black Irish.[41] Following an influx of immigrants to Galway during the 2000s, approximately 20% of the population is non-Irish.[41] Slightly more than half of this group (11.3%) are white Europeans, coming from Poland and other Central European and Baltic States, such as Latvia and Lithuania. Smaller numbers of Asian and African immigrants come from East Africa, Nigeria, Zimbabwe and Sri Lanka. In the 2006 Census, 15.4% of the population were aged 0–14, 76.1% were aged 15–64, and 8.5% were aged over 65. 51.9% of the population were female and 48.1% were male.[42]
Economy[edit]
Galway City is the capital of Connacht. The city has experienced very rapid growth in recent years. Galway has a strong local economy with complementary business sectors, including manufacturing industry, tourism, retail and distribution, education, healthcare and services that include financial, construction, cultural, and professional.
Most (47%) of the people employed in Galway work in either the commerce or professional sector, with a large number (17%) also employed in manufacturing. Most industry and manufacturing in Galway, like the rest of Ireland, is hi-tech (e.g. ICT, medical equipment, electronics, chemicals, etc.), due to the Celtic Tiger economic boom. Companies such as Boston Scientific, Medtronic, EA Games, Cisco and SAP AG have their regional offices or other offices in Galway City and environs. Soon Apple plans to build a massive data centre in Athenry outside Galway City. Tourism is also of major importance to the city, which had over 2.1 million visitors in 2000, and produced revenue of over €400 million.[43]
Transport[edit]
Air[edit]
Galway Airport, located 6 km (3.73 mi) east of the city at Carnmore, ceased to have scheduled passenger flights on 1 November 2011.[44] Because the runway is too short to take modern passenger jet aircraft, its operations are limited.[45] Aerfort na Minna (22 km (13.67 mi) west of the city) operates regular flights to each of the Aran Islands (Oileáin Árann). Shannon Airport (90 km) and Ireland West Airport Knock (86 km) are also within easy reach of the city, both of which have flights around Ireland and to Britain, Continental Europe and North America (from Shannon).
Bus[edit]
Buses are the main form of public transport in the city and county. There are fifteen routes[46] in the city operated by Bus Éireann and City Direct .
Various bus companies also provide links throughout County Galway and nationwide.[47] These operate from a number of locations:
- The main bus and rail station in the city is Ceannt Station.
- Galway Coach Station, located at Fairgreen,[48] is also a coach transport hub. Scheduled direct and commuter services operate between the Coach Station, Dublin and Dublin Airport, as well as services to Limerick, Cork and Clifden. These are operated by Gobus and Citylink.[49][50]
- Other regional bus operators use various bus stops around the city centre, and many serve the NUIG and GMIT campuses as well.
Rail[edit]
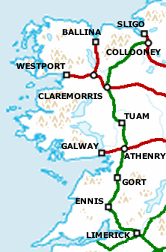
Western Rail Corridor ex-GSWR line south of Limerick in green,
other ex-MGWR lines are in red.
Galway's main railway station is Ceannt Station (Stáisiún Cheannt), which opened in 1851,[51] and was renamed in honour of Éamonn Ceannt in 1966. A major redevelopment, including a completely new urban district, Ceannt Station Quarter,[52][53] has been proposed for the station and adjoining land.
The Midland Great Western Railway reached Galway in 1851, giving the city a direct main line to its Broadstone Station terminus in Dublin. As the 19th century progressed the rail network in Connacht was expanded, making Galway an important railhead. The nearby town of Athenry became a railway junction, giving Galway links to Ennis, Limerick and the south in 1869 and Sligo and the north in 1894. In 1895 the MGW opened a branch line between Galway and Clifden.
The 20th century brought increasing road competition, and this led the Great Southern Railways to close the Clifden branch in 1935. In the 1970s the state railway authority Córas Iompair Éireann closed the Sligo-Athenry-Ennis line to passenger services. It later closed to freight as well.
Iarnród Éireann, Ireland's national rail operator, currently runs six return passenger services each day between Galway and Dublin Heuston, also serving intermediate stations. Travel time is just under 3 hours. Services on the Galway–Limerick line have now resumed, with around 5–6 trains each way per day.
From Galway railway services along the Western Rail Corridor link the city with Ennis, and Limerick where trains run to Cork via Limerick Junction (for Tipperary, Clonmel and Waterford) and Mallow (for Kilarney and Tralee).
Road[edit]
Three national primary roads serve the city: the N17 connecting the Northwest (Tuam, Sligo, Donegal Town, Letterkenny and Derry), the M6 motorway running East/West (Athlone, Dublin), and the M18 motorway linking Galway to Southern towns and cities (Ennis, Shannon Town, Limerick and Cork). As of 2015[update] works are underway to extend the M18 northwards to link to the M6. When completed, the M17/M18 will reduce journey times between Limerick and Galway, allowing the two cities to work more closely together. In addition, there are plans for a semi-ring road of the city, the Galway City Outer Bypass.[54][55] There is also an Inner City Ring (Cuar Inmheánach) route that encircles the city centre, most of which is pedestrianised.
Galway is considered the gateway to Connemara and the Gaeltacht, including Mám, An Teach Dóite, Cor na Móna, Ros Muc, Bearna and An Cheathrú Rua. The N59 along the western shore of Lough Corrib and the R337 along the northern shore of Galway Bay both lead to this largely rural and highly scenic region.
Waterways[edit]
The River Corrib is by far the most important waterway in Galway and a number of canals and channels were built above and through the city. The purposes of these to divert and control the water from the river, to harness its power and to provide a navigable route to the sea.[56] Of these, there were two major schemes – one between 1848 and 1858 and the other during the 1950s. The canals provided a power source for Galway and were the location of the first industries in the mid-19th century. The Eglinton Canal provided a navigation from the sea (at the Claddagh Basin) to the navigable part of the river (above the Salmon Weir Bridge). Most of the mills are still used today for various purposes; for instance, NUI Galway still uses a water turbine for electricity generation for their building on Nun's Island.
Currently, there are four bridges across the Corrib. Following the southward flow of the river these are, from the north: the Quincentennial Bridge, the Salmon Weir Bridge, the William O'Brien Bridge and the Wolfe Tone Bridge. There are plans for a fifth bridge as part of the Galway City Outer Bypass project. The Clare River flows from the North of the County Galway, through Tuam, Claregalway into Lough Corrib.
Harbour[edit]

Galway is the most central port on the West Coast of Ireland in the sheltered eastern corner of Galway Bay.[citation needed] The harbour can be used by vessels up to 10,000 tonnes deadweight (DWT) and the inner dock can accommodate up to 9 vessels at any one time. Pending approval, Galway Harbour may see major changes, should the €1.5 billion development plan go ahead.
Regular passenger ferry and freight services operate between Galway and the tourist destination of the Aran Islands which is home to World Heritage Site Dún Aonghasa. The islands also have regular links with the towns of Rossaveal and Doolin, which are physically closer but far smaller.
Commuter ferry services have been proposed to the tourism town of Kinvara, on the opposite side of Galway Bay.[57]
Major work in the harbour area was carried out in 2009 to accommodate the stopover of the Volvo Ocean Race. This was one of the biggest events ever to visit Galway. The event returned with the finale of the race in June 2012. This was unprecedented in Volvo Ocean Race history.
Education[edit]
In 2002, there were 27 primary schools and 11 secondary schools in Galway.[58]
National University of Ireland, Galway[edit]
National University of Ireland, Galway (NUIG) was founded in 1845 as Queen's College, Galway, and was more recently known as University College, Galway (U.C.G.). It is divided into several colleges including the College of Arts, Social Science and Celtic Studies, the College Medicine, Nursing and Health Sciences, the College of Business, Public Policy and Law, the College of Science and the College of Engineering and Informatics. The university has an enrollment of 16000 (2010).
The Biomedical Research Building was opened in 2014.[59][citation needed] It houses the Regenerative Medicine Institute (REMEDI). Also opened in 2014 were the Hardiman Building and a new School of Psychology. The Hardiman Building is home to the university's collection of more than 350 literary, theatrical, political and historical archives.[citation needed] The building houses also the Moore Institute for Research in the Humanities and Social Sciences and the Whitaker Institute for Innovation and Societal Change. The National Institute of Preventive Cardiology is an affiliate of NUIG.[citation needed]
The offices of the Central Applications Office (C.A.O.) are also located in the city, this being the clearing house for undergraduate college and university applications in the Republic of Ireland; a related organisation, the Postgraduate Applications Centre, processes some taught postgraduate courses.[citation needed]
Galway Mayo Institute of Technology (GMIT)[edit]
GMIT, in addition to having two campuses in Galway City, also has campuses in Castlebar, Letterfrack and Mountbellew. GMIT's Galway campus is based on the Dublin Road in Galway city, overlooking Galway Bay. It is the administrative headquarters for the Institute and has four Schools of study; the School of Business, the School of Engineering, the School of Science & Computing, and the College of Tourism & Arts.[60]
Health[edit]
Publicly funded health care and social services are provided in Galway by the HSE (West) division of the Health Services Executive. The main city hospital, University Hospital Galway, is located on two campuses — Galway University Hospital and Merlin Park University Hospital.[citation needed]
Two private hospitals, The Galway Clinic and the Bon Secours Hospital, Galway, also operate in the city. Galway Hospice provides palliative care for the people of Galway City and County on a homecare, inpatient and daycare basis.[citation needed]
Sport[edit]
Galway has a diverse sporting heritage, with a history in sports ranging from horse racing, Gaelic games, soccer and rugby to rowing, basketball, motorsport, greyhound racing and others. The Galway Races are known worldwide and are the highlight of the Irish horse racing calendar. Over the years it has grown into an annual festival lasting seven days.
Gaelic games[edit]
Both hurling and football are strong in Galway city. Pearse Stadium in Salthill is the home to Galway GAA, the county's Gaelic games body. The Galway hurlers compete annually in the All-Ireland Senior Hurling Championship for the Liam MacCarthy Cup. Despite having won the cup only 4 times in their history, Galway is considered as one of the top teams in the Championship. Galway reached the 2012 All-Ireland final only to draw with Kilkenny to force a replay, the first since 1959, which they eventually lost. The footballers compete annually in the All-Ireland Senior Football Championship for the Sam Maguire Cup. The footballers have won the cup 9 times with the most recent being in 2001.
Association football[edit]
Galway United FC is based in the city and plays in the League of Ireland Premier Division. The team plays its home games at Eamonn Deacy Park. The club was formed in 2013 and first competed in the 2014 season.
The previous tenants of Eamonn Deacy Park, also called Galway United, first competed in the League of Ireland since 1977, then known as Galway Rovers. Michael D. Higgins, later elected President of Ireland in 2011, served as a president of the club in a ceremonial capacity. Following struggles with debts, the club became defunct at the end of the 2011 season. The Galway United Supporters Trust (GUST) had been servicing many debts of the company and were able to keep the club afloat for the 2011 season, with it having been effectively abandoned by its directors. GUST withdrew their support for the team and applied to join the 2012 League of Ireland as a community enterprise, rather than as a private company, which the old club had been. This application was not successful, however.
Galway F.C. was formed the following year from a merger of GUST with Mervue United and Salthill Devon, two other clubs in the city, who had competed in the First Division since 2009 and 2010 respectively.
Rugby[edit]
Professional[edit]
The professional team for the province, Connacht Rugby, is based in the city. The team play their home matches at the Galway Sportsgrounds which is the current provincial Rugby Stadium.
The team participate in the Pro14 League competition, and in season 2015-2016 won their first ever Championship by defeating reigning Champions Glasgow Warriors in the Semi-final and then beating four times champions Leinster Rugby in the Grand Final on 28 May 2016 played at Murrayfield Stadium.[61]
The team participated in European Rugby Champions Cup 2016/2017.[62]
Club (Amateur)[edit]
There are two senior amateur rugby union teams in Galway, Galwegians RFC and Galway Corinthians RFC, who play in the All-Ireland League. There are also two junior clubs, OLBC RFC & NUIG RFC who both participate in the Connacht Junior League.
"Barna Knocknacarra Rugby Club" (or Na Bairneachaí), established in 2007, offers "mini rugby" for children at levels U8 to U12.[63]
Golf[edit]
Several golf courses serve Galway city. Bearna Golf Club, Galway Golf Club, Cregmore Golf Club and Galway Bay Golf Resort are all situated within 8 kilometres (5 mi) of the city centre.
Swimming[edit]
Nearby Salthill has a 25m competitive swimming pool in the Leisureland complex and three competitive swimming clubs (i) Shark Swimming Club, (ii) Laser Swimming Club and (iii) Galway Swimming Club train there. There is also a handball and racketball club while there are several martial arts clubs throughout the city. There is a 25m pool at NUI, Galway as well as one at Renmore's KingFisher Club.
Sailing and rowing[edit]
Sailing on both sea and lake are popular, as is rowing in the River Corrib with seven clubs providing the necessary facilities and organising rowing competitions. These clubs include: Gráinne Mhaol Rowing Club, Tribesmen Rowing Club, Galway Rowing Club, Coláiste Iognáid ('The Jes') Rowing Club, St. Joseph's Patrician College ('The Bish') Rowing Club, NUIG Boat Club and Cumann Rámhaiochta Choláiste na Coiribe.
In 2009 Galway hosted a stopover on the Volvo Ocean Race and the city was finishing point of the round-the-world competition in July 2012.
Greyhound racing[edit]
Near the city centre, on College Road, the Sportsground has greyhound races every Thursday, Friday and Saturday night. It was refurbished by the Irish Greyhound Board, Bord na gCon, and the facility is shared with the Connacht rugby team.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ "William R. Wilde's Loch Coirib – Its Shores and Islands". Galway.net. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Mayor of Galway City". Galway City Council. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
- ^ a b "2013 Report" (PDF). boundarycommittee.ie. 2013.
- ^ a b David B. Quinn "Columbus and the North: England, Iceland, and Ireland", The William and Mary Quarterly, Third Series, Vol 49, No. 2 (April 1992), pp. 278–97
- ^ Kavanagh, Mary. Galway-Gaillimh: a bibliography of the city and county. Galway County Council, 2000.
- ^ a b They were the merchant families of Athy, Blake, Bodkin, Browne, Darcy, Deane, Font, Ffrench, Joyce, Kirwin, Lynch, Martyn, Morris, and Skerrett.
- ^ "The Online Historical Population Reports Project www.histpop.org". cso.ie. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ Lorna Siggins (20 September 2014). "Persecuted Muslims build first mosque in Galway". Irish Times. Retrieved 20 September 2014.
- ^ Corry, Eoghan (2005). The GAA Book of Lists. Hodder Headline Ireland. pp. 186–91.
- ^ "Hotel Meyrick – About". Greatsouthernhotelgalway.com. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ Gay Lynch (2010). Apocryphal and Literary Influences on Galway Diasporic History. Cambridge Scholars Publishing. p. 15.
- ^ "Spanish Arch Galway City Spanish Arch Galway Ireland". galwaycity.galway-ireland.ie. Retrieved 2017-04-25.
- ^ "Education Ireland". Educationireland.ie. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Festivals And Events". thisisgalway.ie.
- ^ Tulca Festival of Visual Arts
- ^ a b c "Atlas 2004 – Section 1" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ MSN Travel UK – 2007's Sexiest Cities
- ^ "2008 Travellers' Choice Destination Awards" (PDF). Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "World Architecture Images- Ireland- Galway". European-architecture.info. 19 June 2006. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ Cahill, Susan (2011). For the Love of Ireland. New York: Ballantine Books. ISBN 9780307778352. Retrieved 29 August 2015.
- ^ "Cora Harrison, The Burren Mysteries". Retrieved 12 February 2014.
- ^ "About the town hall / its history and more". Tht.ie. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Galway Early Music website". Galwayearlymusic.com. 16 March 2000. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Galway Cathedral Recitals website". Recitals.galwaycathedral.ie. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ Tribal Chamber Choir Archived 5 January 2014 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Busan, Galway, Sofia Get UNESCO "City of Film" Designation, 1 December 2014.
- ^ "The glory and the gloom of the Galway Film Fleadh". The Irish Times. 15 July 2014.
- ^ "Galway Film Fleadh - Ireland's leading film festival". Galway Film Fleadh.
- ^ "The 25 Coolest Film Festivals in the World, 2014". MovieMaker Magazine.
- ^ "Galway Early Music". Galway Early Music.
- ^ "Galway Sessions 2015". galwaysessions.com.
- ^ "Home". Galway Garden Festival.
- ^ "Home". galwaychristmasmarket.ie.
- ^ "お菓子好きOLの引き出しの中身は?お菓子編". galwaycommunitypride.com.
- ^ The first Super 8 picture show, Irish Times, 19 June 2010
- ^ "Home Page of The Irish Fly Fair". irishflyfair.com.
- ^ "Galway Hub".
- ^ "Census of Population 2011 Preliminary Results for County Galway" (PDF). Galway County Council Social Inclusion Unit. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 June 2013. Retrieved 28 December 2012.
- ^ "2006 Census results (CSO)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "RTÉ – 'Census shows drift from big five'". RTÉ.ie. 26 April 2007. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ a b Siggins, Lorna (24 September 2009). "Almost 20% of Galway’s citizens are non-Irish". The Irish Times. p. 2. Retrieved 8 October 2009.
- ^ "2006 Census results (CSO) – Male/Female Population". Beyond2020.cso.ie. 16 July 2007. Archived from the original on 25 July 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Galway City Development Board – Galway at the Beginning of the 21st century" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Galway Airport press release". Archived from the original on 4 February 2012. Retrieved 9 February 2012.
- ^ 21 February 2007 Investment in Regional Airports to Aid Balanced Regional Development (Department of Community, Rural and Gaeltacht Affairs) "However, before any major development can take place at Galway Airport, the issue of runway length must be addressed. Galway Airport has the second shortest runway length of all of the regional airports in Ireland used for scheduled flights. The total length of the runway is 1350 m, which means that the number of aircraft types that can use it is limited." – Ministerial statement.
- ^ "Galway City bus service summary". GalwayTransport.info. Retrieved 21 September 2012.
- ^ "National and Regional buses to/from Galway". GalwayTransport.info. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Park at Galway — car park Galway Coach Station". Q-park.ie. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ^ "Gobus Travel non-stop between Galway, Dublin City & Dublin Airport Over 28 daily services from only €10". Gobus.ie. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ^ "Citylink — Home". Citylink.ie. 11 February 2012. Retrieved 26 March 2013.
- ^ "Galway station" (PDF). Railscot – Irish Railways. Retrieved 3 September 2007.
- ^ "CIÉ – 'Galway Station Redevelopment'". Cie.ie. Archived from the original on 26 June 2010. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "CIÉ – 'Ceannt Station Quarter'". IarnródÉireann.ie. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Galway City Outer Bypass – Map" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Galway City Council – Galway City Outer Bypass". Galwaycity.ie. Archived from the original on 21 July 2010. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "Waterways of Galway; – Galway Guide". Galway.net. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ Green Party – Transport Archived 13 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ "Microsoft Word — Atlas 2004 Section1.doc" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 July 2011. Retrieved 12 August 2010.
- ^ "April 2016 - NUI Galway". www.nuigalway.ie. Retrieved 2017-03-10.
- ^ https://www.gmit.ie/about/galway-campus
- ^ "Pro12 final: Connacht 20-10 Leinster". BBC Sport. 28 May 2016. Retrieved 15 August 2016.
- ^ "Champions Cup Pools Revealed". European Professional Club Rugby (EPCR). 29 June 2016. Retrieved 15 August 2016.
- ^ "Club History". Barna Knocknacarra Rugby Club. Retrieved 15 August 2016.
External links[edit]
| Look up Galway in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Galway. |














