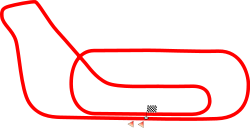
Autodromo Nazionale Monza
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 |
|
| Location | Monza, Italy |
|---|---|
| Time zone | GMT +1 |
| Major Events | F1, GP2, F3, 1000 km Monza, WTCC, SBK |
| Circuit Length | 5.793 km (3.6 mi) |
| Turns | 10 |
| Lap Record | 1:21.046 (Rubens Barrichello, Ferrari, 2004) |
Autodromo Nazionale di Monza is a motorsport race track near the town of Monza, Italy, north of Milan. It is one of the most historic motor racing circuits in the world.
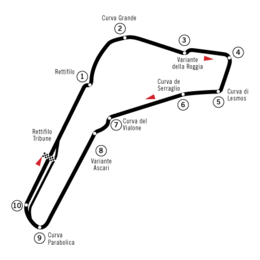
The site has three tracks – the 5.793 km Grand Prix track, the 2.405 km Junior track and a decaying 4.25 km high speed track with steep bankings. Major features of the main track include the Curva di Lesmo, the Curva Parabolica, and the Variante Ascari. The high speed curve, Curva Grande, is located after a slow corner but usually taken flat out by Grand Prix cars.
The circuit, better known for hosting the Formula One Italian Grand Prix, is notable for the fact that drivers are on full throttle for a higher-than-average percentage of the lap due to its long straights and is usually the scenario in which the open-wheeled F1 cars show the raw speed they are capable of (372 km/h during the V10 formula). It is mostly a flat circuit but has a notable, but gradual, gradient from the second Lesmos to the Variante Ascari. Due to the low aerodynamic profile needed, the grip is very low, understeer and the resulting slide can hurt overall speed and are more serious issues than at other circuits, however, the opposite effect, oversteer, is also present in the second sector, requiring the use of a very distinctive opposite lock technique. It is said that drivers can set relatively decent lap times from the beginning without much effort, but in order to set competitive times, drivers must make use of all of their skill at every corner and chicane, since both precision and aggressiveness are required, especially during qualifying. Since horsepower is the key for speed on the straights, only competitors with enough power at their disposal are able to challenge for the top places.
The Monza circuit has been the arena of some of the most tragic episodes in Formula One racing, especially in the early years of the world championship. Since those times, modifications have been introduced to improve spectators safety and reduce curve speed, but it is still criticized by the current drivers by its lack of run-off areas, most notoriously at the chicane that cuts the Variante de la Roggia.
The circuit is also known to be the spiritual home of the Scuderia Ferrari and their passionate supporters, the Tifosi.
Contents |
[edit] History
The first track was built from May to July 1922 by 3,500 workers, financed by the Milan Automobile Club – which created the Società Incremento Automobilismo e Sport (SISA) to run the track. The initial form was a 3.4 km² site with 10 km of macadamized road – comprising a 4.5 km loop track and a 5.5 km road track. The track was officially opened on 3 September 1922 with the second Italian Grand Prix held on 10 September 1922.
In the 1928 Italian Grand Prix the most serious Italian racing accident to date ended in the death of driver Emilio Materassi and 27 spectators. Until 1932, further Grand Prix races were confined to the high-speed loop. The 1933 race was marked by the deaths of three drivers and the Grand Prix layout was changed with two chicanes added and the longer straights removed.
There was major rebuilding in 1938–39, constructing new stands and entrances, resurfacing the track, moving portions of the track and adding two new bends. The resulting layout gave a Grand Prix lap of 6.3 km, in use until 1954. Because of the war, racing at the track was suspended until 1948 and much of the circuit degraded due to lack of attention. It was renovated over two months and held a Grand Prix on 17 October 1948.
[edit] High speed oval
In 1955 work began to entirely revamp the circuit, resulting in a 5.75 km course and a new 4.25 km high-speed oval with banked sopraelevata curves. The two circuits could be combined to create a 10 km long circuit, with cars running parallel on the main straight. The infrastructure was also improved.
The Automobile Club of Italy held 500 mile Race of Two Worlds exhibition competitions on the oval in 1957 and 1958, with three 63 lap heat races each year, races which colloquially became known as the Monzanapolis series. The club's initial intention had been to pit United States Auto Club Championship Cars against European Formula One and sports cars. However, concerns were raised among the European drivers that flat-out racing on the banking would be too dangerous, so ultimately only Ecurie Ecosse and Maserati represented European racing at the first running. The American teams had brought special Firestone tyres with them, reinforced to withstand high-speed running on the bumpy Monza surface, but the Maseratis' steering was badly affected by the larger-than-usual tyre size and so the Modena team withdrew. Ecurie Ecosse's three Jaguar D-type sports cars used their Le Mans-specification tyres with no ill-effects, but were completely out paced. Two heats in 1957 were won by Jimmy Bryan in his Kuzma-Offenhauser Dean Van Lines Special, and the last by Troy Ruttman in the Watson-Offy John Zink Special. In 1958, works Jaguar, Ferrari and Maserati teams appeared alongside the Indy roadsters, but once again the USA cars dominated and Jim Rathmann swept all three races.[1]
Grand Prix returned to this high speed track in 1955, 1956, 1960 and 1961. This last race had another serious accident, with Wolfgang von Trips and fourteen spectators dying near the Parabolica. Despite the fact that the bankings were not involved in that accident, the F1 never raced on the oval again (except in the film Grand Prix made in 1966). New safety walls, rails and fences were quickly added and the refuelling area was moved further from the track. Run-off areas were added to the curves in 1965 after a fatality in the 1000km Monza race, the track layout was not changed until Grand Prix returned in 1966 with new chicanes at the banked curves. The 1000km Monza staged the last event on the banking in 1969. While the banking at the AVUS in Berlin was already destroyed in 1967, the Pista di Alta Velocità is still there, but in a very bad shape. A petition [2] can be signed to keep it from decay or even destruction.
[edit] Layout changes
Both car and Grand Prix motorcycle racing were regular attractions at Monza from 1966, but with increasing speeds the track was "slowed" in 1972 with two more chicanes. Grand Prix motorcycles continued to use the un-slowed road track until two races resulted in five deaths in 1973, including Renzo Pasolini and Jarno Saarinen. Motorcycle racing did not return to Monza until 1981. The 1972 chicanes were soon seen to be ineffective at slowing cars and one was remade in 1974, the other in 1976, and a third also added in 1976, with extended run-off areas. The Grand Prix lap was now 5.8 km long.
With technology still improving vehicle speeds the track was again changed in 1979, with added kerbs, run-off areas extended and tyre-barriers improved, the infrastructure was also upgraded. These changes encouraged world championship motorcycling to return in 1981, but further safety work was undertaken through the 1980s. Also in the 1980s the podium, paddock and pits complex, stands, and campsite were either rebuilt or improved.
In the safety conscious years following the death of Ayrton Senna in 1994 (albeit at a different track), the three main long curves were "squeezed" in order to install larger gravel traps, shortening the lap to 5.77 km. In 1997 the stands were reworked to expand capacity to 115,000.
In 2000 the chicane on the main straight was altered, changing from a double left-right chicane to a single right-left chicane, in an attempt to reduce the frequent accidents at the starts due to the conformation of the braking area. The second chicane was also reprofiled. In the Formula 1 Grand Prix of the same year, the first to use these new chicanes, a marshal was killed by flying debris after a big pileup in the second chicane.
The length of the track in its current configuration is 5.793 km.
On 12 May 2007, Noriyuki Haga made the new lap record for motorcycles 1’44.941 in Superpole on that day. He was riding a Yamaha.
[edit] Deaths from crashes
- 1924 Count Louis Zborowski, killed after crashing into a tree.
- 1928 Emilio Materassi and 27 spectators.
- 1933 Giuseppe Campari, Mario Umberto Borzacchini and Stanislas Czaykowski.
- 1955 Alberto Ascari, driving a Ferrari 750 Monza during private testing. Four days after his crash in the 1955 Monaco Grand Prix.
- 1961 Count Wolfgang von Trips and 14 spectators.
- 1965 Bruno Deserti, killed during Ferrari Official test prior to Le Mans in a Ferrari P2/3 4000 cm3.
- 1965 Tommy Spychiger, Killed during 1000K Sports car race in Ferrari 365P2.
- 1970 Jochen Rindt during qualification practice.
- 1973 Renzo Pasolini, Jarno Saarinen during 250 cc class of GP delle Nazioni.
- 1973 Carlo Chionio, Renzo Colombini and Renato Galtrucco during a race for 500cc Juniores Italian motorcycle championship.
- 1974 Silvio Moser, died in hosiptal one month after suffering injuries at 1000km Monza race.
- 1978 Ronnie Peterson, died in hospital.
- 2000 Paolo Gislimberti, a marshall hit by debris from a first-lap accident.
[edit] Gallery
[edit] External links
- Autodromo Nazionale di Monza
- Site dedicated to the "Sopraelevata" banking, with petition
- Detailed information of the circuit of Monza, detailed map, video on board, virtual and 3D views of the famous curves
- Satellite picture by Google Maps
- Hidden History of Monza's bankings
- Monza History and Statistics
- Ciro Pabón's Racetracks 3D views and virtual laps of all F1 circuits, including this one, via Google Earth
|
|
|
|---|---|
| Current circuits (2008 season) |
Melbourne · Sepang · Bahrain · Catalunya · Istanbul · Monte Carlo · Montreal · Magny-Cours · Silverstone · Hockenheim · Hungaroring · Valencia · Spa · Monza · Singapore · Fuji · Shanghai · Interlagos |
| Future circuits |
New: Yas Island (2009) · South Jeolla (2010) — Returning: Nürburgring (2009) · Suzuka (2009) |
| Former circuits |
A1-Ring · Adelaide · Ain-Diab · Aintree · Anderstorp · AVUS · Brands Hatch · Bremgarten · Buenos Aires · Caesars Palace · Clermont-Ferrand · Dallas · Detroit · Dijon · Donington Park · East London · Estoril · Imola · Indianapolis · Jacarepaguá · Jarama · Jerez · Kyalami · Le Mans · Long Beach · Mexico City · Monsanto · Montjuïc · Mont-Tremblant · Mosport Park · Nivelles-Baulers · Oporto · Österreichring · Paul Ricard · Pedralbes · Pescara · Phoenix · Reims · Riverside · Rouen · Sebring · TI · Watkins Glen · Zandvoort · Zeltweg · Zolder |
|
|
|---|
|
Current circuits (2008 season) : Former circuits (2005 - 2007) : |
|
|
|---|
|
Former Tracks (1956-1981) Road Courses International |
|
|
|---|
|
Current Circuits (2008) Former Circuits: Official Test Track: |
|
|
|---|
|
Current Circuits (2008): |
|
|
|---|
|
Current Circuits (2008): |